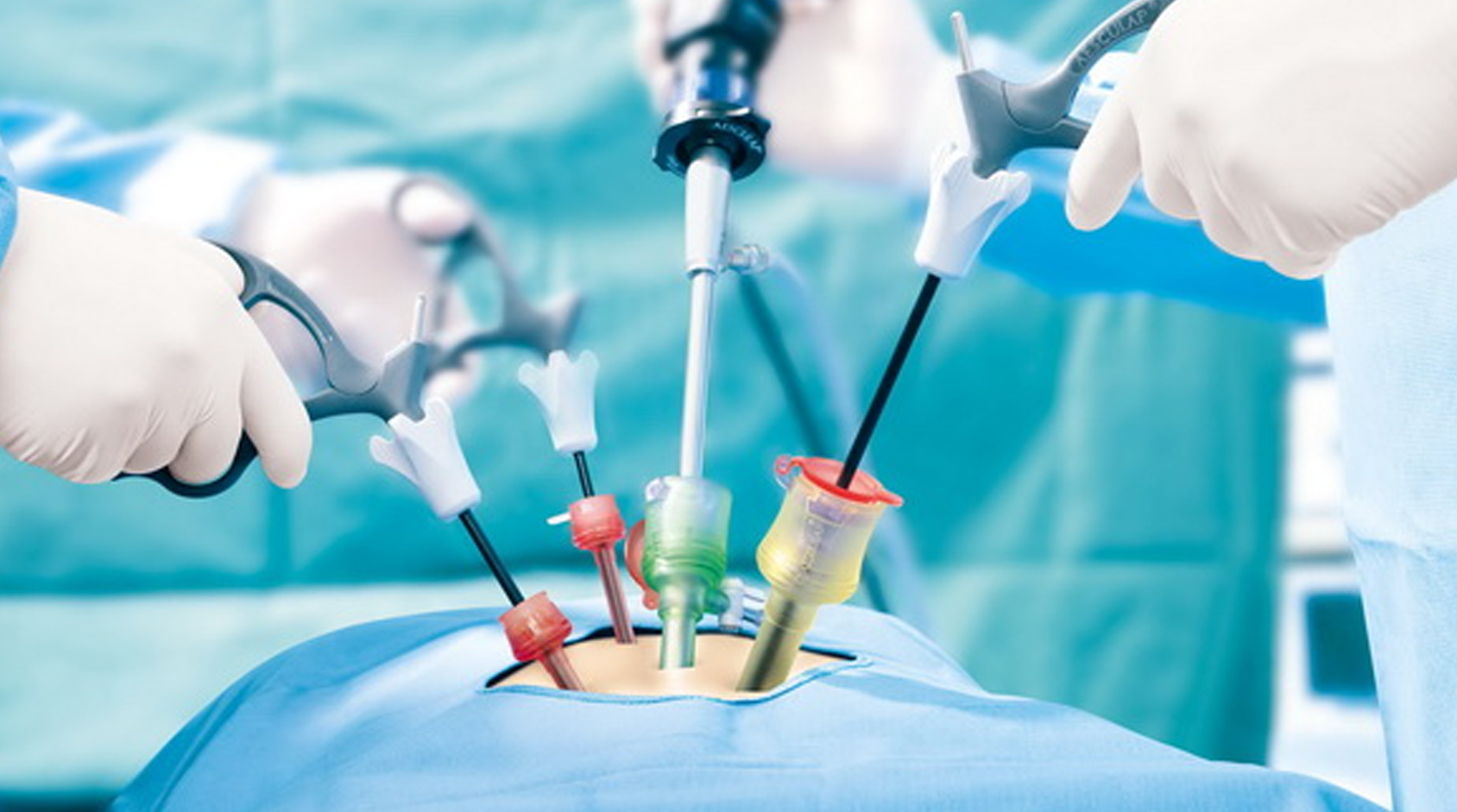
Diagnostic and operative laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are two minimally invasive procedures used to diagnose and treat various gynecological conditions.
Diagnostic laparoscopy involves the insertion of a thin, lighted scope through a small incision in the abdomen to examine the pelvic organs, such as the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. This procedure can help diagnose conditions such as endometriosis, pelvic adhesions, ovarian cysts, and uterine fibroids.
Operative laparoscopy, on the other hand, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a laparoscope to perform surgeries such as removal of ovarian cysts, tubal ligation, treatment of endometriosis, and removal of ectopic pregnancies. This procedure involves making several small incisions in the abdomen through which specialized surgical instruments are inserted to perform the surgery.
Similarly, hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive diagnostic and operative procedure that involves the insertion of a thin, lighted scope through the vagina and cervix to examine the inside of the uterus. Hysteroscopy can be used to diagnose and treat conditions such as uterine fibroids, polyps, and abnormal bleeding.
Operative hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to perform surgeries such as removal of uterine polyps or fibroids, septum resection, and endometrial ablation. This procedure involves inserting specialized surgical instruments through the hysteroscope to perform the surgery.
Both laparoscopy and hysteroscopy offer several advantages over traditional open surgery. They are minimally invasive, requiring smaller incisions, and usually result in less pain, scarring, and a shorter recovery time. Patients also typically experience less bleeding and fewer complications.
Patients undergoing laparoscopy or hysteroscopy will usually receive anesthesia to ensure comfort during the procedure.
Before undergoing laparoscopy or hysteroscopy, patients will need to prepare by fasting for a certain amount of time before the procedure and following specific instructions given by their healthcare provider. After the procedure, patients will need to rest for a period of time before being discharged from the hospital or outpatient facility.
Possible complications from laparoscopy or hysteroscopy are rare, but they can include bleeding, infection, damage to internal organs, and reaction to anesthesia. Patients should notify their healthcare provider immediately if they experience any unusual symptoms following the procedure, such as fever, severe pain, or heavy bleeding.
In conclusion, diagnostic and operative laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are minimally invasive procedures used to diagnose and treat various gynecological conditions. These procedures offer several advantages over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, less pain, scarring, and a shorter recovery time. Patients undergoing laparoscopy or hysteroscopy will need to prepare beforehand and should be aware of the possible complications associated with the procedure. Overall, these procedures are effective options for patients requiring diagnosis and treatment of gynecological conditions.